
AI can be used to help mitigate the negative impacts of climate change and protect the environment, but there are risks and challenges that need to be carefully considered
Bukhari Zulfiqar Shah
Xian Jiaotong University, China
“Environmental law is the ultimate expression of environmental ethics and protection. It is how we translate our values into concrete action for the benefit of the environment, the economy, and society.” – Sheila Watt-Cloutier, Canadian Inuit activist and Nobel Peace Prize nominee.
Environmental laws are regulations and policies designed to protect the environment and natural resources from harm or degradation. These laws govern a wide range of activities, from pollution control to wildlife conservation.

Artificial intelligence (AI) has a significant role to play in mitigating the negative impacts of climate change and protecting the environment helping us to address environmental issues, such as climate change, air and water pollution, and the depletion of natural resources. AI can be used in a variety of ways to achieve these goals, from predicting climate change patterns and reducing energy consumption to monitoring wildlife populations and identifying environmental risks. However, as with any technology, AI also has the potential to cause harm to the environment and exacerbate existing problems if not properly regulated.
AI can also be used to reduce energy consumption in a variety of settings
One of the most important applications of AI in the context of the environment is in predicting and mitigating the effects of climate change. Climate models that incorporate AI can be used to analyze large amounts of data from a variety of sources and make accurate predictions about future climate patterns. This information can be used to inform policy decisions and guide the development of strategies to reduce carbon emissions and minimize the impact of climate change.
 AI can also be used to reduce energy consumption in a variety of settings. Smart home devices, for example, can be programmed to adjust lighting, heating, and cooling systems automatically based on occupancy and ambient temperature, reducing energy waste. Similarly, AI can be used in industrial and commercial settings to optimize energy usage and reduce waste.
AI can also be used to reduce energy consumption in a variety of settings. Smart home devices, for example, can be programmed to adjust lighting, heating, and cooling systems automatically based on occupancy and ambient temperature, reducing energy waste. Similarly, AI can be used in industrial and commercial settings to optimize energy usage and reduce waste.
Despite the many potential benefits of AI for the environment, there are also potential risks and challenges associated with its use. For example, AI systems may be vulnerable to bias and may perpetuate or amplify existing inequalities in the distribution of environmental risks and benefits. Additionally, the energy consumption associated with training and running AI models may contribute to carbon emissions, offsetting some of the potential benefits of their use.
 Pakistan has a comprehensive legal framework for environmental protection and conservation. The framework consists of various laws, policies, and regulations that aim to protect the environment and promote sustainable development. The Constitution of Pakistan provides for the protection of the environment as a fundamental right. Article 9 of the Constitution states that every citizen has the right to a clean and healthy environment.
Pakistan has a comprehensive legal framework for environmental protection and conservation. The framework consists of various laws, policies, and regulations that aim to protect the environment and promote sustainable development. The Constitution of Pakistan provides for the protection of the environment as a fundamental right. Article 9 of the Constitution states that every citizen has the right to a clean and healthy environment.
Pakistan ranked 142 out of 180 countries in terms of overall environmental quality
The Pakistan Environmental Protection Act, 1997 is the primary legislation for environmental protection in the country. The Act provides for the prevention and control of pollution, conservation of natural resources, and protection of the environment. It establishes the Pakistan Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) as the regulatory authority responsible for enforcing environmental standards and regulations. In addition to the Pakistan Environmental Protection Act, there are several other laws and regulations that address specific environmental issues. To ensure the effective implementation of environmental laws, Pakistan has established various institutions, including the EPA and SEPA, to regulate and monitor environmental issues. The government has also established environmental tribunals to hear and adjudicate environmental cases.
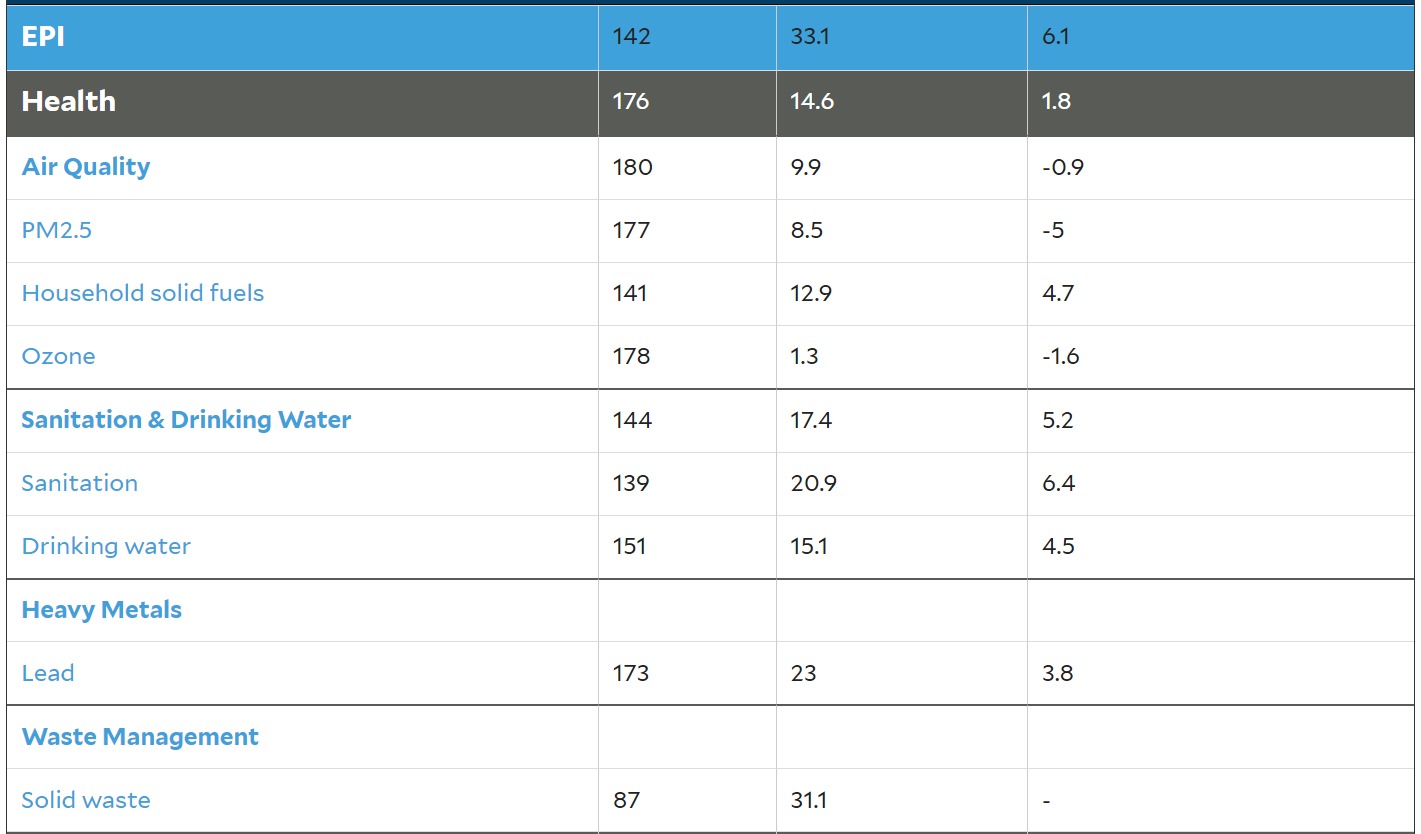 According to the Environmental Performance Index (EPI) 2020, which ranks countries based on their environmental performance, Pakistan ranked 142 out of 180 countries in terms of overall environmental quality. In terms of air quality specifically, Pakistan ranked 153 out of 180 countries. Additionally, according to the World Air Quality Report 2020, which measures particulate matter (PM2.5) pollution levels in cities around the world, Pakistan had several cities that ranked among the most polluted in the world, including Lahore, Faisalabad, and Karachi. These rankings suggest that Pakistan faces significant challenges when it comes to pollution and environmental quality.
According to the Environmental Performance Index (EPI) 2020, which ranks countries based on their environmental performance, Pakistan ranked 142 out of 180 countries in terms of overall environmental quality. In terms of air quality specifically, Pakistan ranked 153 out of 180 countries. Additionally, according to the World Air Quality Report 2020, which measures particulate matter (PM2.5) pollution levels in cities around the world, Pakistan had several cities that ranked among the most polluted in the world, including Lahore, Faisalabad, and Karachi. These rankings suggest that Pakistan faces significant challenges when it comes to pollution and environmental quality.
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is a major infrastructure and development project that aims to connect China’s western region to Pakistan’s Gwadar port through a network of highways, railways, and pipelines. While the project promises significant economic benefits for Pakistan, it also raises concerns about its impact on the environment. The construction of CPEC infrastructure, such as highways and power plants, could result in environmental degradation, including deforestation, air and water pollution, and soil erosion. These environmental impacts could have long-term consequences for the health and well-being of local communities, as well as for the natural ecosystems in the region.
The government must ensure that the environmental impact assessments are conducted rigorously, and that the mitigation measures are effectively implemented and enforced
 To address these concerns, the Pakistani government has taken steps to integrate environmental protection into the CPEC project. The government has established the China-Pakistan Joint Cooperation Committee (JCC) on Environment to oversee the environmental impact of CPEC projects and ensure compliance with environmental laws and regulations. The government has established the CPEC Environmental Protection Fund to finance environmental protection and conservation efforts in the CPEC region. The fund aims to promote sustainable development and protect the environment by supporting research, capacity building, and community participation. But there are concerns about the effectiveness of these measures in ensuring environmental protection in the CPEC project.
To address these concerns, the Pakistani government has taken steps to integrate environmental protection into the CPEC project. The government has established the China-Pakistan Joint Cooperation Committee (JCC) on Environment to oversee the environmental impact of CPEC projects and ensure compliance with environmental laws and regulations. The government has established the CPEC Environmental Protection Fund to finance environmental protection and conservation efforts in the CPEC region. The fund aims to promote sustainable development and protect the environment by supporting research, capacity building, and community participation. But there are concerns about the effectiveness of these measures in ensuring environmental protection in the CPEC project.
The government must ensure that the environmental impact assessments are conducted rigorously, and that the mitigation measures are effectively implemented and enforced. It is also important to involve local communities in decision-making processes related to CPEC projects to ensure their concerns about the environment are adequately addressed. The government also need to develop the Pakistan Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) regulations, which necessitate environmental impact assessments for all CPEC projects. The EIAs will assess the potential environmental impact of the project and propose mitigation measures to minimize those impacts promptly.
 Pakistan also needs to timely invest in capacity building of regulatory agencies and other stakeholders to better understand the environmental impacts of AI systems and develop effective regulations to address those impacts. The government can also promote public awareness and education campaigns to raise awareness of the environmental impacts of AI and the importance of responsible and sustainable use of AI systems.
Pakistan also needs to timely invest in capacity building of regulatory agencies and other stakeholders to better understand the environmental impacts of AI systems and develop effective regulations to address those impacts. The government can also promote public awareness and education campaigns to raise awareness of the environmental impacts of AI and the importance of responsible and sustainable use of AI systems.
AI has the potential to contribute significantly to achieving environmental sustainability goals by facilitating decision-making, improving resource efficiency, and reducing waste. As AI becomes more integrated into environmental management.
- Air pollution regulations: AI can be used to monitor air pollution levels in real-time and identify sources of pollution. This data can be used to inform policy decisions and help enforce air pollution regulations more effectively.
- Waste management: AI can be used to optimize waste management systems and reduce the amount of waste that goes to landfills. Environmental laws may need to be updated to encourage the adoption of AI-based waste management systems.
- Water quality regulations: AI can be used to monitor water quality and identify sources of contamination. This data can be used to inform policy decisions and help enforce water quality regulations more effectively.
- Biodiversity conservation: AI can be used to monitor wildlife populations and identify areas of high conservation value. Environmental laws may need to be updated to require the use of AI-based tools in biodiversity conservation efforts.
- Climate modeling: AI can help climate scientists more accurately model and predict future climate scenarios, which can inform policy decisions and help us better understand the impacts of climate change.
- Energy optimization: AI can be used to optimize energy use in buildings, transportation systems, and manufacturing processes, reducing energy waste and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Sustainable agriculture: AI can help optimize crop yields while reducing water and fertilizer use, reducing the environmental impacts of agriculture.
- Circular economy: AI can support the transition to a circular economy, where waste is minimized, and resources are reused and recycled, by providing insights into supply chain optimization, product design, and reuse.
 To address these concerns, many countries around the world are developing or updating their environmental laws and regulations to take into account the impact of AI on the environment. it will be important to ensure that existing environmental laws are updated to account for the new technologies and their potential impacts. Here are some examples of environmental laws that may need to be upgraded and integrated with AI, some of the key issues that these laws and regulations address include:
To address these concerns, many countries around the world are developing or updating their environmental laws and regulations to take into account the impact of AI on the environment. it will be important to ensure that existing environmental laws are updated to account for the new technologies and their potential impacts. Here are some examples of environmental laws that may need to be upgraded and integrated with AI, some of the key issues that these laws and regulations address include:
- a) Data privacy and security: AI systems rely heavily on data, and the collection and processing of this data can have environmental impacts. Environmental laws and regulations must ensure that personal and sensitive data is protected and that AI systems are secure to prevent data breaches that could harm the environment.
- b) Energy consumption: AI systems can consume significant amounts of energy, and the energy used to power these systems can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Environmental laws and regulations may require AI systems to meet certain energy efficiency standards to reduce their environmental impact.
- c) Environmental monitoring: AI systems can be used to monitor environmental conditions and detect changes, such as changes in air quality or the spread of invasive species. Environmental laws and regulations may require the use of AI systems for monitoring and reporting purposes.
- d) Environmental impact assessments: Environmental laws and regulations may require companies to conduct environmental impact assessments before deploying AI systems that could have a significant impact on the environment.
In conclusion, AI can be used to help mitigate the negative impacts of climate change and protect the environment, but there are risks and challenges that need to be carefully considered. It is important to use AI in an equitable and sustainable way. Integrating AI into environmental management can improve the effectiveness of laws and regulations, but it is important to update these laws to account for new technologies and potential environmental impacts. Responsible and sustainable use of AI can benefit both people and the planet.
_______________
About Author
 Bukhari Zulfiqar Shah belongs to Khairpur Mirs, and is an advocate of high court Sindh, currently doing Ph.D. in International Environmental Law from Xian Jiaotong University, China. He did Graduation in Commerce, LLB, MA Journalism, and MA Sociology from Shah Abdul Latif University Khairpur, and did LLM from Zhejiang University, China. Email: advbukhari@gmail.com
Bukhari Zulfiqar Shah belongs to Khairpur Mirs, and is an advocate of high court Sindh, currently doing Ph.D. in International Environmental Law from Xian Jiaotong University, China. He did Graduation in Commerce, LLB, MA Journalism, and MA Sociology from Shah Abdul Latif University Khairpur, and did LLM from Zhejiang University, China. Email: advbukhari@gmail.com
[…] Also read: Artificial intelligence and the Environmental Laws Need to Be Upgraded and Integrated […]